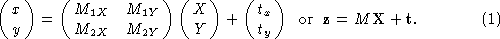



The 2D affine projection from scene to image can then be written in its most general form as
Here is the image point,
is the image point,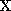 is a 2D scene point, and
M
,
is a 2D scene point, and
M
, constitute the camera matrix parameters, which we will term the
motion
parameters because they represent the camera/scene motion over time. The
2D affine reconstruction problem for point features is: given
constitute the camera matrix parameters, which we will term the
motion
parameters because they represent the camera/scene motion over time. The
2D affine reconstruction problem for point features is: given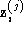 for multiple features
i
in multiple images
j
, determine the motion
for multiple features
i
in multiple images
j
, determine the motion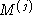 ,
,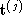 and structure
and structure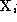 . We shall add the subscripts
l
and
r
to refer to left/right image quantities, so that we have camera matrix
parameters
. We shall add the subscripts
l
and
r
to refer to left/right image quantities, so that we have camera matrix
parameters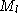 ,
,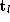 ,
,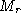 and
and . Stereo 2D affine projection is illustrated in figure
1
.
. Stereo 2D affine projection is illustrated in figure
1
.
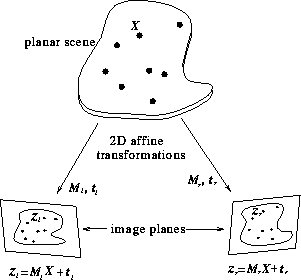
Figure 1:
Stereo affine 2D projection from planar scene to image planes.
Given complete data for
n
features over
k
images, Tomasi & Kanade's algorithm [
18
] achieves the optimal solution for a 3D affine reconstruction. It also
generalizes simply to the 2D problem by taking the biggest two singular
vectors instead of the biggest three. Thus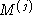 and
and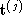 ,
, and
and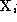 .
.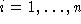 may computed simply using the SVD, This is quite efficient for a small
number of images; however it is a batch algorithm, and the speed
degrades quickly as more image data is added. As we have previously
demonstrated [
12
], the variable state dimension filter algorithm achieves virtually the
same accuracy, but has the advantages of being recursive, not requiring
complete data, and allowing new features to be added to the
reconstruction as they appear and discarded features to be removed. We
thus employ the Tomasi/Kanade algorithm on the first stereopair of our
image sequence, and thereafter use the simplest version of the VSDF as
presented in [
12
]. Details may be found in [
11
].
may computed simply using the SVD, This is quite efficient for a small
number of images; however it is a batch algorithm, and the speed
degrades quickly as more image data is added. As we have previously
demonstrated [
12
], the variable state dimension filter algorithm achieves virtually the
same accuracy, but has the advantages of being recursive, not requiring
complete data, and allowing new features to be added to the
reconstruction as they appear and discarded features to be removed. We
thus employ the Tomasi/Kanade algorithm on the first stereopair of our
image sequence, and thereafter use the simplest version of the VSDF as
presented in [
12
]. Details may be found in [
11
].



Adrian F Clark