 and the state dimension
N
. It is also necessary to estimate temporal informations like the number
of self-transitions of each state, and the order of the transitions
between canonical postures.
and the state dimension
N
. It is also necessary to estimate temporal informations like the number
of self-transitions of each state, and the order of the transitions
between canonical postures.


Automatic gesture recognition consists, at this point, in finding the
model that best fits a given image sequence. This implies estimating the
following parameter set: the transition matrix
A
, the posture models collection
C
, the variance matrix and the state dimension
N
. It is also necessary to estimate temporal informations like the number
of self-transitions of each state, and the order of the transitions
between canonical postures.
and the state dimension
N
. It is also necessary to estimate temporal informations like the number
of self-transitions of each state, and the order of the transitions
between canonical postures.
The identification procedure is based on the Expectation-Maximization
(EM) algorithm [
1
]. It computes the update of the model parameters and it estimates some
auxiliary quantities, such as the number of jumps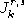 from state
r
to state
s
up to time
k
and the occupation time
from state
r
to state
s
up to time
k
and the occupation time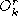 of state
r
up to time
k
.
of state
r
up to time
k
.
The convergence of the EM algorithm is guaranteed by Jensen inequality [ 1 ]. The generated sequence of the estimates of the parameters correspond to nondecreasing values of an appropriate likehood function. The learning process can, then, be terminated when the likehood either reaches a certain threshold level or does not increase any more.
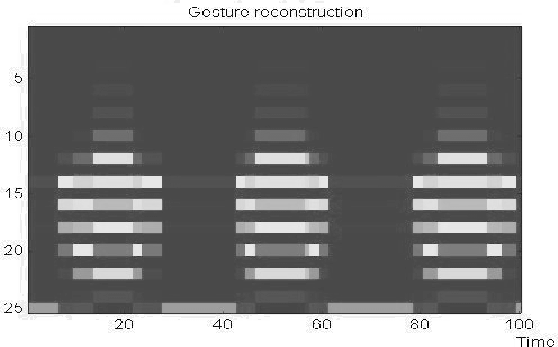
Let's consider the simple example of a hand gesture shown in Figure (6). It consists of repeated openings and closures of the hand.

|

|
 , the gray levels are proportional to the values of the components of
the observation vectors.
, the gray levels are proportional to the values of the components of
the observation vectors.
|



Adrian F Clark