


Next:
5 Recognition results
Up:
Distinctive Descriptions for Face
Previous:
3 Recognition Method
The experimental database, described below, consists of training, test
and difficult test images. To judge the accuracy of normalisation eye
location is assessed. Since the eye can swivel and close, the centre of
the eye socket is used as a fixed reference point.
|
Eye location accuracy
|
|
Set of faces
|
% within 5 pixels
|
|
Training
|
92
|
|
Normal test
|
85
|
|
Difficult test
|
72
|
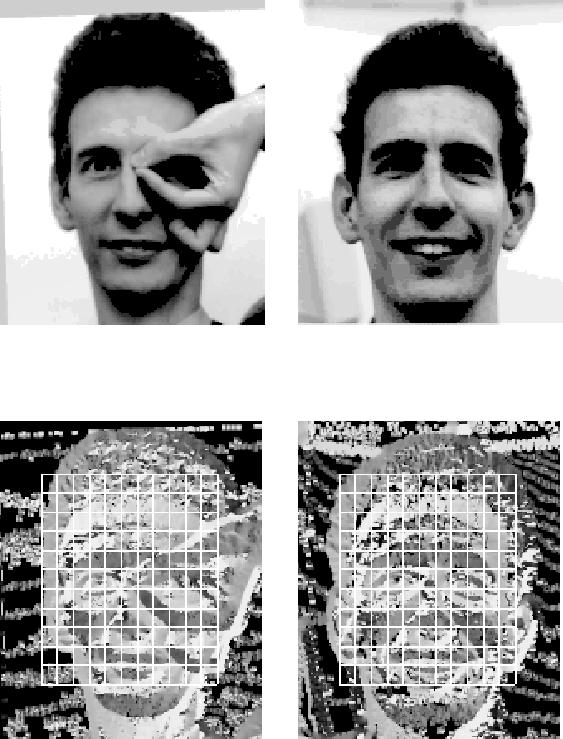
Figure 1:
The top left image is a normalised difficult test face. It is correctly
matched to the training face on its right which has also been
normalised. Below each face is the corresponding orientation image.
These display the orientation of the gradient vector. The images are
darkest for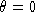 and brightest for
and brightest for . If the gradient magnitude is zero, the orientation can not be found
and, for this display, the pixel is set to the lowest intensity. The
grid is for
n
=11
. If the gradient magnitude is zero, the orientation can not be found
and, for this display, the pixel is set to the lowest intensity. The
grid is for
n
=11
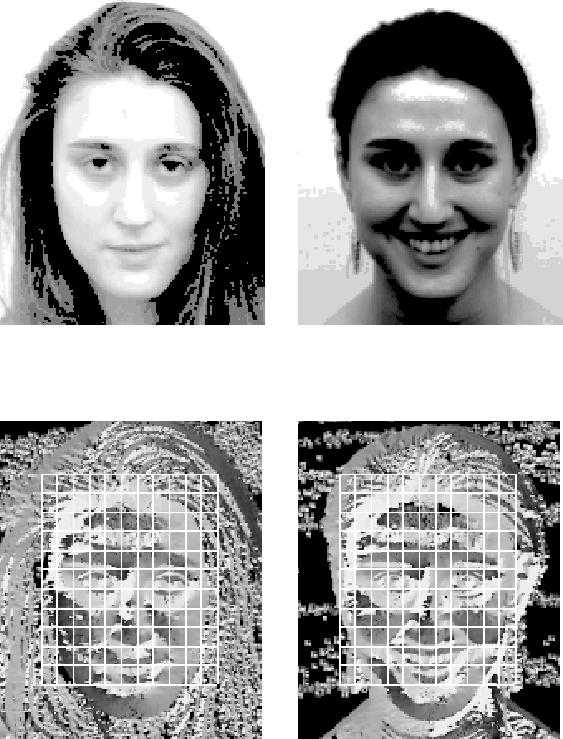

Figure 2:
The face in the top left is a normal test image. It is correctly matched
to the training face on the right. Both faces have been normalised. Note
the stability of the orientation images.



Next:
5 Recognition results
Up:
Distinctive Descriptions for Face
Previous:
3 Recognition Method
Hond D A
Fri Jul 11 14:14:48 BST 1997

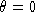 and brightest for
and brightest for . If the gradient magnitude is zero, the orientation can not be found
and, for this display, the pixel is set to the lowest intensity. The
grid is for
n
=11
. If the gradient magnitude is zero, the orientation can not be found
and, for this display, the pixel is set to the lowest intensity. The
grid is for
n
=11


