Transport
Machine vision has application in many aspects of transport. For
example, it can be used to collect and understand data useful in
transport planning and safety. It can also play an active role in
navigation and vehicle guidance.
Traffic Monitoring
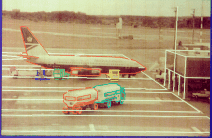 Monitoring traffic is a vital part of transport planning. Human
observers are currently used, but this approach is time consuming and
the data captured limited. An automated system to study traffic
movements is being developed which aims to identify vehicles entering an
area under observation, and monitor their movements and manoeuvres.
Using images from a single camera, vehicles can, thereby, be located
precisely and tracked as it moves in the scene. To obtain information on
the actual position of the vehicles, the system is given a model of the
scene and the exact position of the camera. Using this geometrical
knowledge, a full understanding of vehicle movements can be obtained for
subsequent analysis.
Monitoring traffic is a vital part of transport planning. Human
observers are currently used, but this approach is time consuming and
the data captured limited. An automated system to study traffic
movements is being developed which aims to identify vehicles entering an
area under observation, and monitor their movements and manoeuvres.
Using images from a single camera, vehicles can, thereby, be located
precisely and tracked as it moves in the scene. To obtain information on
the actual position of the vehicles, the system is given a model of the
scene and the exact position of the camera. Using this geometrical
knowledge, a full understanding of vehicle movements can be obtained for
subsequent analysis.
Aerial Navigation
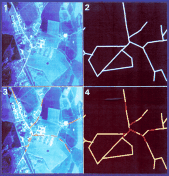 At present, the navigation of airborne vehicles relies on the use of
active remote sensing equipment. These techniques are very expensive and
an automated system to interpret aerial images, using passive image
sensing, combined with machine vision techniques, is being developed.
The system operates by identifying road networks in the scene below (Fig
1), and matching them with stored maps of the roads in the area (Fig 2).
The roads are identified by processing the image with computational
filters that pick out road-like features (Fig 3). Further processing
modifies the roads into a series of straight line segments. The
characteristics and relationships between these segments can be compared
with the stored map which has been similarly processed (Fig 4). This
system can work over a range of altitudes and has potential use in the
autonomous guidance of aircraft.
At present, the navigation of airborne vehicles relies on the use of
active remote sensing equipment. These techniques are very expensive and
an automated system to interpret aerial images, using passive image
sensing, combined with machine vision techniques, is being developed.
The system operates by identifying road networks in the scene below (Fig
1), and matching them with stored maps of the roads in the area (Fig 2).
The roads are identified by processing the image with computational
filters that pick out road-like features (Fig 3). Further processing
modifies the roads into a series of straight line segments. The
characteristics and relationships between these segments can be compared
with the stored map which has been similarly processed (Fig 4). This
system can work over a range of altitudes and has potential use in the
autonomous guidance of aircraft.
Transport Safety
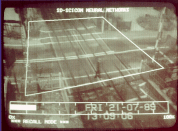 Video monitoring by human operators is applied widely to transport
safety. This activity is labour intensive, and operators are prone to
fatigue. Machine vision, however, is now capable of providing valuable
assistance by drawing attention to predefined events of interest.
Systems using neural nets possess the flexibility to ignore acceptable
events, but to generate an alarm in unacceptable situations. To do this,
the neural net must be trained to accept the normal range of lighting
and visibility likely in an outdoor situation. Events such as intruders,
or obstructions in the scene, can then be identified by the system. To
make the system more robust, training continues whilst it is in place.
This allows it to adapt to slowly changing situations, while retaining
its sensitivity to unacceptable occurrences.
Video monitoring by human operators is applied widely to transport
safety. This activity is labour intensive, and operators are prone to
fatigue. Machine vision, however, is now capable of providing valuable
assistance by drawing attention to predefined events of interest.
Systems using neural nets possess the flexibility to ignore acceptable
events, but to generate an alarm in unacceptable situations. To do this,
the neural net must be trained to accept the normal range of lighting
and visibility likely in an outdoor situation. Events such as intruders,
or obstructions in the scene, can then be identified by the system. To
make the system more robust, training continues whilst it is in place.
This allows it to adapt to slowly changing situations, while retaining
its sensitivity to unacceptable occurrences.
 At present, the navigation of airborne vehicles relies on the use of
active remote sensing equipment. These techniques are very expensive and
an automated system to interpret aerial images, using passive image
sensing, combined with machine vision techniques, is being developed.
The system operates by identifying road networks in the scene below (Fig
1), and matching them with stored maps of the roads in the area (Fig 2).
The roads are identified by processing the image with computational
filters that pick out road-like features (Fig 3). Further processing
modifies the roads into a series of straight line segments. The
characteristics and relationships between these segments can be compared
with the stored map which has been similarly processed (Fig 4). This
system can work over a range of altitudes and has potential use in the
autonomous guidance of aircraft.
At present, the navigation of airborne vehicles relies on the use of
active remote sensing equipment. These techniques are very expensive and
an automated system to interpret aerial images, using passive image
sensing, combined with machine vision techniques, is being developed.
The system operates by identifying road networks in the scene below (Fig
1), and matching them with stored maps of the roads in the area (Fig 2).
The roads are identified by processing the image with computational
filters that pick out road-like features (Fig 3). Further processing
modifies the roads into a series of straight line segments. The
characteristics and relationships between these segments can be compared
with the stored map which has been similarly processed (Fig 4). This
system can work over a range of altitudes and has potential use in the
autonomous guidance of aircraft.